流程简介
mybatis的使用步骤:
- 引入mybaits依赖
- 编写mybatis全局配置文件
- 编写dao层接口
- 编写mapper.xml,与接口中的方法绑定
- 获取SqlSessionFactory
- 从SqlSessionFactory中获取SqlSession
- 从SqlSession中获取与相应接口对应的Mapper类
- 调用接口中的方法
- 关闭资源
框架的一般原理:启动程序,读取配置文件,保存配置文件的信息,根据配置文件构造bean,在使用框架的功能时期,所有的配置文件的信息都被保存或者转化为其他的信息保存了起来。然后根据框架提供的api,调用框架的方法实现功能。mybatis也是如此:
在获取 SqlSessionFactory 后,就将配置文件中的信息保存了起来,在一个 org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration 的实例中。
获取SqlSessionFactory
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| String resource= "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream in= Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in);
```
首先,new一个SqlSessionFactory对象,然后将配置文件的输入流作为参数调用build方法。调用以下方法
```java
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
|
在1处,获取一个XMLConfigBuilder会用它来解析xml文件,实际上是一个XMLMapperEntityResolver对象;
在2处,进行解析会调用parseConfiguration方法(见下)。可以看见解析的就是在mybatis-config.xml中的各个标签,而且有一定的顺序。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
loadCustomVfs(settings);
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
|
将从配置文件中获取的数据保存到configuration字段中。
以mapper标签举例:根据标签内不同的属性(url,package,resource)处理。将获取的数据添加到configuration中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else {
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
} else {
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
}
|
Configuration中的数据:可以从中找到所有的配置文件的信息,如果没有配置,那么从中可以看见有默认值或者为null。例如cacheEnabled = true
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
| protected Environment environment;
protected boolean safeRowBoundsEnabled;
protected boolean safeResultHandlerEnabled = true;
protected boolean mapUnderscoreToCamelCase;
protected boolean aggressiveLazyLoading;
protected boolean multipleResultSetsEnabled = true;
protected boolean useGeneratedKeys;
protected boolean useColumnLabel = true;
protected boolean cacheEnabled = true;
protected boolean callSettersOnNulls;
protected boolean useActualParamName = true;
protected boolean returnInstanceForEmptyRow;
protected String logPrefix;
protected Class <? extends Log> logImpl;
protected Class <? extends VFS> vfsImpl;
protected LocalCacheScope localCacheScope = LocalCacheScope.SESSION;
protected JdbcType jdbcTypeForNull = JdbcType.OTHER;
protected Set<String> lazyLoadTriggerMethods = new HashSet<String>(Arrays.asList(new String[] { "equals", "clone", "hashCode", "toString" }));
protected Integer defaultStatementTimeout;
protected Integer defaultFetchSize;
protected ExecutorType defaultExecutorType = ExecutorType.SIMPLE;
protected AutoMappingBehavior autoMappingBehavior = AutoMappingBehavior.PARTIAL;
protected AutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior autoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior = AutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior.NONE;
protected Properties variables = new Properties();
protected ReflectorFactory reflectorFactory = new DefaultReflectorFactory();
protected ObjectFactory objectFactory = new DefaultObjectFactory();
protected ObjectWrapperFactory objectWrapperFactory = new DefaultObjectWrapperFactory();
protected boolean lazyLoadingEnabled = false;
protected ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new JavassistProxyFactory();
protected String databaseId;
protected Class<?> configurationFactory;
protected final MapperRegistry mapperRegistry = new MapperRegistry(this);
protected final InterceptorChain interceptorChain = new InterceptorChain();
protected final TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = new TypeHandlerRegistry();
protected final TypeAliasRegistry typeAliasRegistry = new TypeAliasRegistry();
protected final LanguageDriverRegistry languageRegistry = new LanguageDriverRegistry();
protected final Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements = new StrictMap<MappedStatement>("Mapped Statements collection");
protected final Map<String, Cache> caches = new StrictMap<Cache>("Caches collection");
protected final Map<String, ResultMap> resultMaps = new StrictMap<ResultMap>("Result Maps collection");
protected final Map<String, ParameterMap> parameterMaps = new StrictMap<ParameterMap>("Parameter Maps collection");
protected final Map<String, KeyGenerator> keyGenerators = new StrictMap<KeyGenerator>("Key Generators collection");
protected final Set<String> loadedResources = new HashSet<String>();
protected final Map<String, XNode> sqlFragments = new StrictMap<XNode>("XML fragments parsed from previous mappers");
protected final Collection<XMLStatementBuilder> incompleteStatements = new LinkedList<XMLStatementBuilder>();
protected final Collection<CacheRefResolver> incompleteCacheRefs = new LinkedList<CacheRefResolver>();
protected final Collection<ResultMapResolver> incompleteResultMaps = new LinkedList<ResultMapResolver>();
protected final Collection<MethodResolver> incompleteMethods = new LinkedList<MethodResolver>();
protected final Map<String, String> cacheRefMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
|
environment中就是配置的环境的信息

mapperRegistry中存放者已经注册的Mapper:其中有这个对应的接口的信息
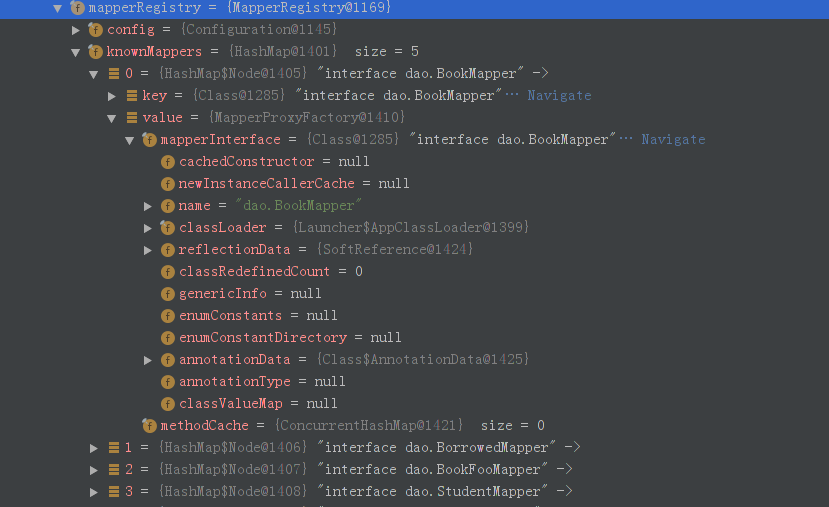
mappedStatements是一个mapper标签中每一条标签的键值对,键是对应的方法(包含段名和全名,当短名冲突的时候会以一个Ambiguity对象填充),值是关于这一条mapper的封装,包括Configuration,sqlSource(源sql语句)还有resultMap,ParamMap等。
总而言之,SqlSessionFactory中包含着所有的配置文件的信息,在以后的使用中都需要这些配置。
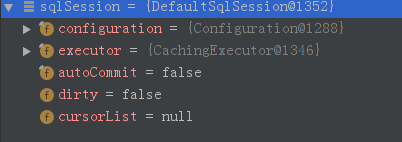
获取SqlSession
总说SqlSession线程不安全,为什么呢。加入两个线程,第一个线程执行到一半的时候宁外一个线程提交了次sqlSession,那么加入第一个线程中的又出现了错误呢?
1
| SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
|
调用以下方法:
获取环境,事务工厂,事务,Executor
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx);
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
|
根据ExecutorType(一个枚举类型:SIMPLE, REUSE, BATCH)获取不同的Executor,然后判断是否开启类缓存,包装Executor,增加执行时sql语句时的缓存的逻辑,添加插件。Executor是一个sql语句执行器,执行增删改查。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
|
sqlSession中的成员: